
Understanding Sickle Cell Disease: Causes, Symptoms, And Diagnosis
Causes
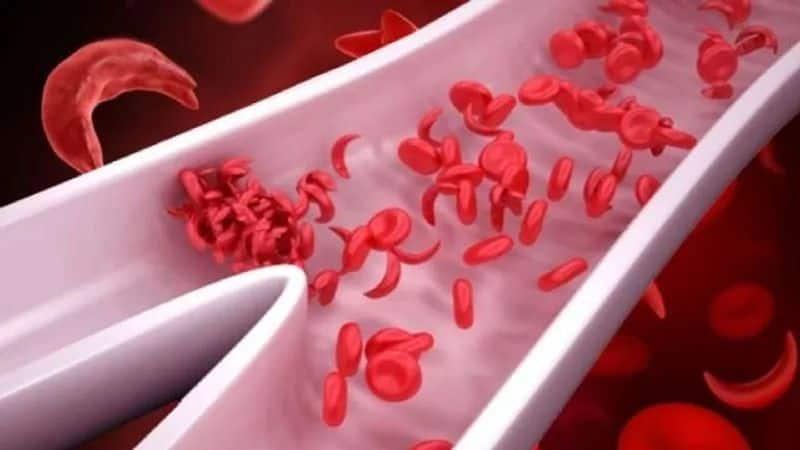
- Primarily caused by when the haemoglobin-beta gene undergoes mutation. In chromosome 11, adenine to thymine goes through single nucleotide substitution. This results in abnormal haemoglobin levels in the body causing the formation of sickle cells. Autosomal recessive inheritance pattern is also known as a cause of sickle cell disease. This can be understood as - the child receiving two mutated genes from each parent, leading to SCD development. Someone with a family history of sickle cell disease is prone to high risk because it is hereditary in nature
Symptoms
Symptoms of sickle cell disease include –
- Pain that is chronic in nature. Pain can affect the chest, legs and arms commonly. It can also cause swelling in some parts of the body Experiencing pain in bones, especially in long bones. This occurs because of bone marrow infraction Anaemia-related conditions such as splenic sequestration increases reticulocyte count. It can prove fatal in the long run as red blood cells does nor carry enough oxygen in body. Jaundice signs such as skin and eyes becoming yellow in colour In children it can manifest as growth retardation Sickle cell disease also can cause chronic fatigue and paleness of skin Severe complications like difficulty in breathing, blood clots, stroke and even organ failure can be caused due to sickle cell disease.
Also Read:
Stop smelly fart: Top 7 foods to avoid for better digestion
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Sickle cell disease can be conducted through methods such as –
- Imaging studies such as – radiography, MRI and CT scanning can be used. Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) is mandated by the US to be conducted to understand any abnormalities in a fetus. Experts suggest haemoglobin electrophoresis for diagnosis of SCD Laboratory tests such as – serum electrolytes that measure minerals essential for the functioning of the body like calcium or potassium and haemoglobin solubility testing High-performance liquid chromatography can help separate types of haemoglobin in the blood sample. DNA analysis can recognize any mutation in genes. For individuals with a family history of SCD, this test can identify risks. Peripheral blood smear is a microscopic examination. Blood observed under a microscope can be identified for any sickle-shaped red blood cells.
- By Dr Byreddy Poojitha - Hemato Oncologist & Bone Marrow Transplant - Cancer Specialist, CARE Hospitals Hitech City
Also Read:
International Olympic Day 2024: Know date, time, history, significance
Legal Disclaimer:
MENAFN provides the
information “as is” without warranty of any kind. We do not accept
any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images,
videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information
contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright
issues related to this article, kindly contact the provider above.















Comments
No comment