
Where Are The Main Growth Drivers And Regional Trends In Brazil Carbon Market?
-
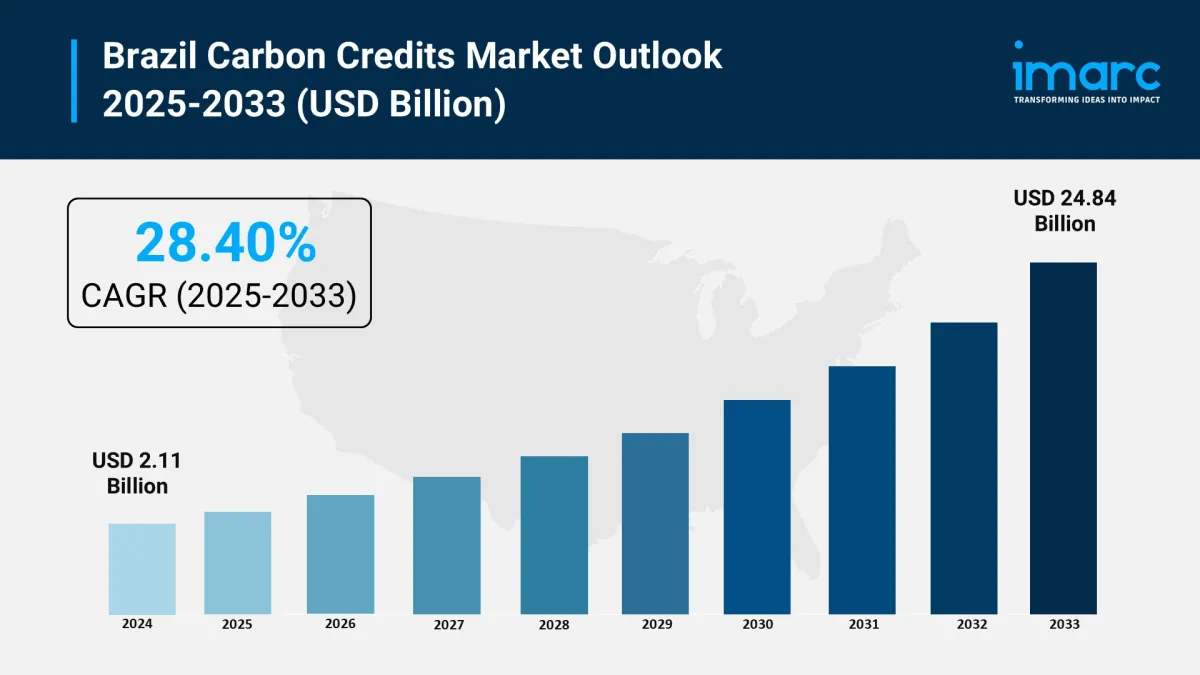
Market Size in 2024: USD 2.11 billion
Market Forecast in 2033: USD 24.84 billion
CAGR (2025-2033): 28.40%
Brazil Carbon Credits Market Structure:
-
Regulated Market: Limits emissions. Companies can trade Brazilian Emission Quotas (CBEs) and Verified Emission Reduction Certificates (VERCs).
Voluntary Market: Companies can voluntarily offset emissions. They use credits from REDD+ (reducing deforestation) and forest restoration projects.
-
Global Demand: Article 6 of the Paris Agreement and standards like Verra and CDM attract foreign investment.
Corporate Sustainability: Petrobras is investing USD 120 million in credits to achieve net-zero goals.
Policy Incentives: Tax incentives, like Rio de Janeiro's ISS Neutral Law, increase participation. The Green Rural Product Note (CPR Verde) also supports this effort.
Sectoral Focus:
-
Forestry and Land Use: Over 60% of Brazil's emissions are from agriculture and land-use changes. So, REDD+ and reforestation are important credit sources.
Agriculture Exemption: Primary agricultural activities aren't part of the regulated market. This is because there are measurement issues. However, they can join voluntary markets.
Industry and Energy: Key compliance targets are the oil, cement, and steel sectors. These industries emit over 25,000 tCO2e per year.
Opportunities:
-
Indigenous and Community Benefits: The law lets Indigenous and traditional communities sell credits from their lands. Also, 5% of fines will support these communities.
Global Leadership: Brazil's diverse wildlife and the LuxCS Triple C Protocol boost its image for top-quality credits.
Biofuel Integration: CBIOs under RenovaBio (18 million registered by 2020) support biofuel-related credits.
Challenges:
-
Regulatory Delays: Progress on SBCE regulations is slow. Key elements are expected by July 2025.
Market Integrity: Worries about greenwashing and poor-quality credits need strong verification. This includes checks by Verra and LuxC.
Land Ownership: Laws are tricky, and without community input, risks grow. For example, Para's $180 million deal shows this issue clearly.
Agriculture Exclusion: Critics say it's a problem to leave out agriculture. It has high emissions.
Notable Initiatives:
-
Petrobras' Entry: Bought credits from the Envira Amazonia project. This protects 39,000 hectares of rainforest.
State Programs: Tocantins and Amazonas lead in REDD+ programs. Tocantins even trades credits globally.
Hosting COP30 in Belém in 2025 speeds up regulations and attracts global attention.
Download a sample copy of the report: https://www.imarcgroup.com/brazil-carbon-credits-market/requestsample
Brazil can lead the global carbon credits market. It has strong natural assets and new regulations. However, it must overcome challenges like unclear rules and market trust.
Market SegmentationThe report has segmented the market into the following categories:
Type Insights:
-
Compliance
Voluntary
Project Type Insights:
-
Avoidance/Reduction Projects
Removal/Sequestration Projects
Nature-based
Technology-based
End-Use Industry Insights:
-
Power
Energy
Aviation
Transportation
Buildings
Industrial
Others
Regional Insights:
-
Southeast
South
Northeast
North
Central-West
-
In May 2025, AgriCapture launched its first rice carbon project. This project took place in Brazil's Rio Grande do Sul and was done with NatCap. The initiative helped local farmers use methane-reducing irrigation methods. This access allowed them to tap into international carbon markets. As a result, Brazil's role in generating nature-based carbon credits grew stronger.
In December 2024, Brazil enacted Law 15,042/2024, establishing the SBCE carbon market. It focused on 5,000 companies that emit more than 10,000 tCO2 each year. It required them to report their emissions and allowed for carbon credit trading. This increased regulatory clarity and made Brazil an important player in global markets.
In September 2024, Google bought carbon removal credits from Mombak, a Brazilian startup. They plan to purchase 50,000 metric tons of these credits by 2030. Mombak buys degraded land from farmers and ranchers. It also partners with them to replant native species in the Amazon rainforest.
In September 2024, Amazon and five other companies pledged $180 million. This money will buy carbon offset credits. The goal is to protect the Amazon rainforest in Brazil's Para state. You can buy credits from the LEAF Coalition. The money will help protect forests and support local communities. This is a big step in fighting climate change. It happens during a global drop in carbon credit demand. Tech giants are also putting money into nature-based solutions.
About Us:
IMARC Group is a worldwide management consulting firm. We help ambitious changemakers make a lasting impact. The company provides a comprehensive suite of market entry and expansion services.
IMARC offers a wide range of services. These include:
-
Market assessments
Feasibility studies
Company incorporation help
Factory setup support
Regulatory approvals and licensing
Branding
Marketing and sales strategies.
Competitive landscape and benchmarking
Pricing and cost research
Procurement research
Each service helps businesses succeed in their markets.
Contact Us:
IMARC Group
134 N 4th St., Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
Email: sales[@]imarcgroup.com
Tel No: (D) +91 120 433 0800
United States: +1-631-791-1145
Legal Disclaimer:
MENAFN provides the
information “as is” without warranty of any kind. We do not accept
any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images,
videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information
contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright
issues related to this article, kindly contact the provider above.

















Comments
No comment