
TNR Gold NSR Royalty Update - Los Azules Feasibility Study Confirms Economically Robust Copper Project With Leading ESG Performance
| Table 1: Mineral Reserve Statement, Effective Date September 3, 2025 | ||||
| | | Grade | Contained Metal | |
| Reserve Class | Tonnage (Kt) | Total Cu % | Soluble Cu % | Cu M lb |
| Proven | 229,879 | 0.683 | 0.495 | 3,463 |
| Probable | 793,173 | 0.386 | 0.259 | 6,754 |
| Total | 1,023,052 | 0.453 | 0.312 | 10,217 |
Table 1 Notes:
- The Qualified Person for the Mineral Reserve estimates is Gordon Zurowski P.Eng., an AGP employee. Mineral Reserves have an effective date of 03 September 2025. Mineral Reserves are reported on a 100% basis.
- Mineral Reserves are estimated assuming open pit mining methods and include dilution. Recoveries were based on the extractions shown in Figure 2. Pit slopes vary by sector and range from 32° to 37°. The cut-off is variable and ranges from $4.79/t NSR to $7.23/t NSR. The copper price used was $4.25/lb Cu. Cu recovery varies by lithology. Mining costs vary by bench with a minimum of $2.14/t and a maximum of $4.11/t. Processing costs are variable and range from $3.18/t to $5.62/t leached. The processing costs include: $1.61/t G&A, $0.43/t leached for sustaining capital, and $0.15/t leached to account for closure cost. Copper cathode sales cost is $0.02/lb Cu. Copper cathode was assumed to be sold FOB the mine site.
Updated Mineral Resource Estimate
The database for resource estimation has a cutoff date of March 27, 2025. An additional 1,075 meters of drilling from four geotechnical holes, completed from early 2025 to date, were not included in the resource estimate.
The mineral resources have been classified according to guidelines and logic set out in the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum (CIM 2019) Definitions referred to in NI 43-101. Resources were classified as Measured, Indicated or Inferred by considering the geology, sampling, and grade estimation aspects of the model. For geology, consideration was given to the confidence in the interpretation of the lithologic domain boundaries and geometry. For sampling, consideration was given to the number and spacing of composites, the orientation of drilling and the reliability of sampling. For the estimation results, consideration was given to the confidence with which grades were estimated, as measured by the quality of the match between the grades of the data and the model.
Mineral resources are determined using an NSR cut-off value to cover the processing cost for each recovery methodology. For supergene and primary material using sulfuric acid leaching and SX/EW recovery, a marginal cut-off was used that was variable ranging from $4.79/t NSR to $7.23/t NSR. The supergene and primary material can be treated in a float mill with NSR cutoffs of $5.13/t and $5.11/t, respectively. NSR values are based on a copper price of $4.80/lb, gold at $2,500/oz and silver at $32/oz where applicable. Variable pit slopes between 32° and 37° were applied depending on sector.
The current database is sufficient for preparing a long-range model that will serve as a basis for modeling associated with completing the FS. The extent of mineralization along strike exceeds three kilometers, and the distance across strike is approximately one kilometer. The deposit is open at depth. Over the approximately 2.5 km strike length where mineralization is strongest, the average drill spacing ranges from approximately 50 meters to more than 120 meters. The central core of the enriched zone is drilled at an approximate 50 m spacing. The assay database considers 627 drillholes with 132,255 meters of assayed intervals. Resource estimation work was performed using Datamine Studio software.
Resources disclosed in Table 2 are reported in two categories related to processing amenability:
1) materials that are suited for processing in a commercially proven conventional, ambient conditions, copper bio-leaching scheme (Leach); and
2) materials that are better suited to processing either in a more advanced bio-leaching scheme such as Nuton® Technology or traditional milling/concentrator approach (Mill or Leach+).
| Table 2: Mineral Resources (Exclusive of Mineral Reserves), Effective Date September 3, 2025 | |||||||||
| | | Million tonnes (MT) | Average Grade | Contained Metal | |||||
| | | | CuT % | CuSol % | Au (g/t) | Ag (g/t) | Cu (Blbs) | Au (Moz) | Ag (Moz) |
| Measured & Indicated | Supergene Leach | 251.9 | 0.303 | 0.167 | - | - | 1.7 | - | - |
| Supergene Mill or Leach+ | 77.6 | 0.108 | 0.042 | 0.04 | 1.11 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 2.8 | |
| Primary Mill or Leach+ | 635.9 | 0.255 | 0.046 | 0.05 | 1.17 | 3.6 | 0.9 | 23.8 | |
| Total Measured & Indicated | Leach & Mill or Leach+ | 965.5 | 0.255 | 0.077 | | | 5.4 | 1.0 | 26.6 |
| Inferred | Supergene Mill or Leach+ | 601.1 | 0.292 | 0.131 | 0.04 | 1.32 | 3.9 | 0.9 | 25.5 |
| Primary Mill or Leach+ | 3,638.2 | 0.201 | 0.027 | 0.04 | 1.06 | 16.1 | 4.9 | 124.5 | |
| Total Inferred | Leach & Mill or Leach+ | 4,239.3 | 0.214 | 0.042 | | | 20.0 | 5.7 | 149.9 |
Notes to Table 2 :
- The Qualified Person for the Mineral Resource estimate is Jeff Sullivan - CRM-SA, LLC. Mineral Resources have an effective date of September 3, 2025. Mineral resources, which are not mineral reserves, do not have demonstrated economic viability. The estimate of mineral resources may be materially affected by environmental, permitting, legal, title, socio-political, marketing, or other relevant factors. The quantity and grade of reported inferred mineral resources in this estimation are uncertain in nature and there is insufficient exploration to define these inferred mineral resources as an indicated or measured mineral resource; it is expected that further infill drilling will result in upgrading the majority of this material to an indicated or measured classification. Reasonable prospects of eventual economic extraction are demonstrated by using a calculated NSR value in each block to evaluate an open pit shell using Measured, Indicated and Inferred blocks in Geovia WhittleTM pit optimization software. Mining costs vary by bench with a minimum of $2.14/t and a maximum of $6.38/t. NSR was calculated using the following: metal prices of $4.80/lb for copper, $2,500/oz for gold and $32/oz for silver, Processing costs are variable and range from $3.18/t to $5.62/t leached. Milling process cost are $5.13/t for supergene and $5.11/t for primary ores. Total freight costs of $150/t for concentrate, selling costs of $0.02/lb for copper. A marginal cut-off was used that was variable ranging from $4.79/t NSR to $7.23/t NSR based on extraction of the resource from the enriched zone using sulfuric acid leaching and SX/EW recovery; the recovery was calculated using the extractions shown in Figure 2 and applying a 95% operational efficiency. The supergene and primary material can potentially be treated in a mill/concentrator with NSR cut-offs of $5.13/t for supergene and $5.11/t for primary respectively. The mill has the added benefit of also recovering the gold and silver present in the resource. Additional parameters are used for the NSR calculation for this scenario. Mill recoveries for the secondary copper resources were 89.3% and for the primary resources were 93.2%. Depending on the potential depth of the pit, total pit slope angles ranged from 32° to 37° depending on the sector. Overburden slopes were set at 32°. Composites of 2 m length were capped where needed; the capping strategy is based on the distribution of grade which varies by location (i.e. domain or proximity to controlling structures) and the associated potential metal removal. The resource estimate is based on uncapped copper grades; local capped grades are used for gold and silver. Block grades were estimated using a combination of ordinary Kriging and inverse distance squared weighting depending on domain size. Model blocks are 20 m x 20 m x 15 m in size.
4. Metallurgy & Recovery
The metallurgical development for the Los Azules feasibility was completed in three phases:
Phase 1 : Baseline testing from the test work program outlined in the 2023 PEA.
Phase 2 : Testing using samples from the 2021-2022 drilling campaigns, to expand the variability database from Phase 1 and to extend the geometallurgical data set to include lithologic domains.
Phase 3 : Scale-up validation using samples from the 2022-2023 exploration campaigns, to validate scale-up from the baseline 3-meter columns to the planned 9-meter bench height of the heap leach pad and to confirm extraction within the test programs. The Phase 3 master composites were built by lithologic domain and were pulled from within the pit shell for the initial five years of operation. Additional samples were collected from the 2023-2024 exploration campaign from holes drilled vertically.
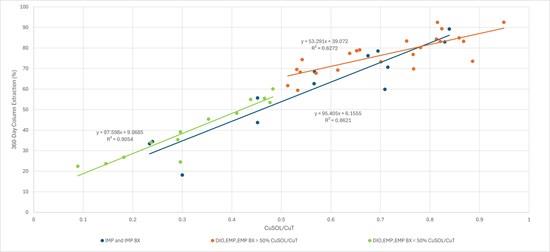
The metallurgical work completed to date provides comprehensive understanding of the expected performance characteristics of the Los Azules deposit. The anticipated copper extractions shown in Figure 2 are utilized in the block model to calculate NSR value for each block in conjunction. Copper recovered to cathodes will consider a heap efficiency and inventory factor of 95% of the extractable copper, based on general experience and industry practice.
Figure 2: All 360-day column extraction data plotted as soluble copper (CuSOL) to total copper (CuT) ratio of the head grade broken out by lithology and ratios.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
Notes: IMP = Intermineral Porphyry, IMP BX = IMP Breccia, DIO = Diorite, EMP = Early Mineral Porphyry, and EMP BX = EMP Breccia
The expected overall total copper recovery is approximately 70.8% and is distributed over a three-year timeframe from placement on the leach pad to account for the timing of active leaching cycles as the pad is constructed. The copper extraction methodology best reflects the potential variability related to host rock materials and the expected variability related to copper grades, mineralogy and recovery that can be practically applied in the mining modeling. In the opinion of the QP, the metallurgical test work and analysis support the metallurgical assumptions provided and used in the mineral reserve statement, the feasibility mine plans, and the economic analysis presented in this report.
Processing of the primary ores can be achieved by using both the Nuton process, alternative leaching processes such as chloride leaching or by using a conventional milling operation to produce concentrates. The advantage of conventional milling is the additional revenue from the recovered gold and silver from the deposit. The next stage of metallurgical test work will include sufficient work to evaluate the processing method to be used for the primary ores during the detailed engineering and initial operations phase.
5. Economic Analysis
Economic Metrics
All currency shown in the FS is expressed in constant Q2 2025 United States Dollars unless otherwise noted.
The Business Case for the leach project uses a copper price assumption of $4.35/lb. Summary results are provided below in Table 3.
| Table 3: Project Metrics - Business Case | ||
| Project Metric | Unit | Number |
| Mine Life | Years | 21 |
| Tonnes Processed | Billion tonnes | 1.023 |
| Tonnes Waste Mined | Billion tonnes | 1.684 |
| Strip Ratio | | 1.65 |
| Total Copper Grade (CuT) | % CuT | 0.453% |
| Soluble Copper Grade (CuSOL) | % CuSOL | 0.312% |
| Total Copper Recovery | % | 70.8% |
| Copper Production (LOM avg.) | tonnes/yr | 148,200 |
| Copper Production (Yrs 1-5) | tonnes/yr | 204,800 |
| Copper Production - cathode Cu | ktonnes | 3,279 |
| Initial Capital Cost | USD Millions | $3,168 |
| Sustaining Capital Cost | USD Millions | $2,131 |
| Closure Costs | USD Millions | $386 |
| C1 Cost (Life of Mine) | USD/lb Cu | $1.71 |
| All-in Sustaining Costs (AISC) | USD/lb Cu | $2.11 |
| Before Taxes | | |
| Net Cumulative Cashflow | USD Millions | $12,721 |
| Internal Rate of Return (IRR) | % | 24.3% |
| Net Present Value (NPV) @ 8% | USD Millions | $4,280 |
| After Taxes | | |
| Net Cumulative Cashflow | USD Millions | $9,647 |
| Internal Rate of Return (IRR) | % | 19.8% |
| Net Present Value (NPV) @ 8% | USD Millions | $2,940 |
| Pay Back Period | Years | 3.87 |
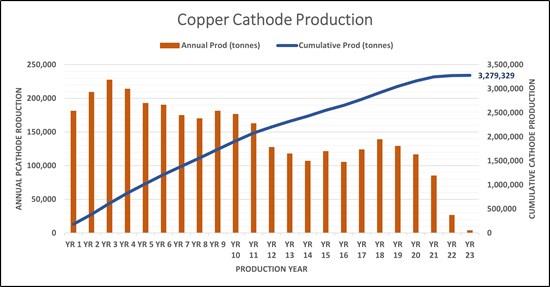
The FS for Los Azules envisions an average annual copper cathode production of 451 million lbs per year (204,800 tonnes) during the first five years of operation, representing an increase of 50 million lbs per year compared to the initial five years of the 2023 PEA production schedule. Over the 21-year life of mine, the average annual copper cathode production is projected at 327 million lbs per year (148,200 tonnes).
Based on the LOM extraction of mineralized material containing approximately 10.2 billion lbs (4.63 million tonnes) of total copper, and an average copper recovery of 70.8%, total copper recoverable to cathode is 7.23 billion lbs (3.28 million tonnes). The copper production by year is shown in Figure 3:
Figure 3: Copper Cathode Production by Year
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
Other economic metrics:
- Initial capital expenditure $3.17 billion Project capital intensity $9.18/ lb Cu per year (or $20,200/ t Cu per year) based on Initial capital / average annual production, or $0.73/ lb Cu (or $1,600/ t Cu) based on LOM Capex / LOM production(8). Average EBITDA(9) per year $1.31 billion for Years 1-5 and $696 million for Years 6-21.
A Nuton® Technology Case is considered in the opportunity section of the FS as a separate project at a PEA-level of study. That case would process primary material stockpiled during the mining of the leach project and mineral resources outside of the Mineral Reserve pit with low soluble copper content. The Nuton case would use the existing processing facilities to support the operation, with a new leach pad and Pregnant Leach Solution pumped back to the original solvent exchange & electrowinning facility. The use of Nuton® Technology has the potential to extend the life of the project and will continue to be evaluated after the conclusion of the FS.
Sensitivity Analysis
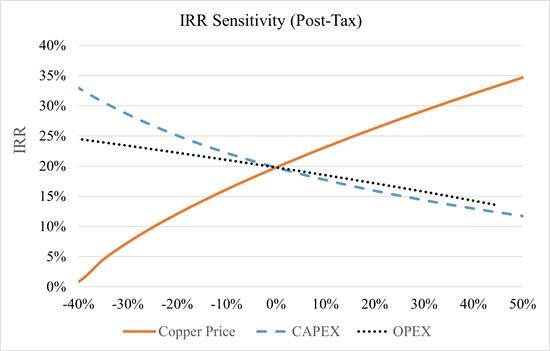
The leach project economics remain attractive (i.e. with an after-tax IRR of 15% or above) at a copper price above $3.74 per pound and are similarly resistant to an increase in LOM capital expenditure of up to 25% and an increase in operating expenses of up to 37% (see Figure 4 below).
Table 4 below shows the sensitivity of the leach project's after-tax economics to copper price fluctuations (+/- 20%). The project after-tax NPV8% is breakeven at a copper price of $3.10 per pound.
| Table 4: Project Copper Price Sensitivity | ||||
| Sensitivity to Change in | Metal Pricing | After-Tax | ||
| Cu Price | Copper Price | NPV | IRR | Payback |
| (%) | $ Cu/lb | $M | % | Years |
| -20% | $3.48 | $902 | 12% | 5.78 |
| -15% | $3.70 | $1,411 | 14% | 5.15 |
| -10% | $3.92 | $1,921 | 16% | 4.68 |
| -5% | $4.13 | $2,430 | 18% | 4.33 |
| 0% | $4.35 | $2,940 | 19.8% | 3.87 |
| 5% | $4.57 | $3,449 | 21% | 3.59 |
| 10% | $4.79 | $3,956 | 23% | 3.39 |
| 15% | $5.00 | $4,461 | 25% | 3.23 |
| 20% | $5.22 | $4,966 | 26% | 3.06 |
Table 5 below shows the sensitivity of the project economics to initial and sustaining capital expenditure escalation on an after-tax basis.
| Table 5: Project Initial & Sustaining CAPEX Sensitivity | |||
| Sensitivity to Increased CAPEX (%) | After-Tax | ||
| | NPV | IRR | Payback |
| | $M | % | Years |
| 0% | $2,940 | 19.8% | 3.87 |
| 5% | $2,773 | 19% | 4.18 |
| 10% | $2,606 | 18% | 4.41 |
| 15% | $2,440 | 17% | 4.60 |
| 20% | $2,273 | 16% | 4.78 |
| 25% | $2,107 | 15% | 4.99 |
Table 6 below shows the sensitivity of the project economics to operating expenditure escalation on a after-tax basis.
| Table 6: Project OPEX Sensitivity | |||
| Sensitivity to Increased OPEX (%) | After-Tax | ||
| | NPV | IRR | Payback |
| | $M | % | Years |
| 0 | $2,940 | 19.8% | 3.87 |
| 5% | $2,746 | 19% | 4.00 |
| 10% | $2,553 | 18% | 4.18 |
| 15% | $2,359 | 18% | 4.32 |
| 20% | $2,166 | 17% | 4.43 |
| 25% | $1,973 | 16% | 4.54 |
Figure 4: Chart of IRR Sensitivity (After-Tax) Relative to Copper Price, CAPEX and OPEX
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
6. Capital & Operating Costs
Capital Costs Estimates
The project includes the development of an open pit mine with multi-stage crushing and screening, a heap leach pad, and a copper solvent extraction-electrowinning (SX/EW) facility with a nominal production capacity of 215 ktpa copper cathodes (design maximum 240 ktpa). Initial capital infrastructure for the Base Case includes the following facilities:
- Mine development and associated infrastructure Coarse rock storage and ore handling (crushing, conveying, agglomeration) Heap leach pads and conveyor stacking systems SX/EW facility Sulfuric acid plant On-site utilities and ancillary facilities including a construction camp Off-site infrastructure: power transmission line (outsourced), access roads, and permanent camp
The Project's initial capital costs are based on budgetary quotes for major equipment, recent in-house cost information and installation factors, and regional contractor inputs and facilities obtained between Q2 and Q3 2025. The capital costs for the project are summarized in Table 5 and should be viewed with the level of accuracy expected for a Feasibility Study.
Design allowances for materials quantities and labor and contingencies were included in the project estimate.
| Table 7: Project Initial Capital Cost | |
| Description | Cost ($M) |
| Direct On-Site Facilities | |
| Mine Facilities, Equipment, Pre-Production | $805.9 |
| Ore Storage & Handling | $283.3 |
| Heap Leach | $331.6 |
| SX-EW | $188.5 |
| Sulfuric Acid Plant | $114.3 |
| Ancillary Facilities | $123.4 |
| Site Development & Yard Utilities | $101.6 |
| Water Supply | $29.6 |
| Direct Off-Site Facilities | |
| Power Supply (see below) | -0- |
| Local Support Facilities | $16.4 |
| Access Roads | $93.6 |
| Logistics Activities Zone (LAZ) | $45.6 |
| Total Direct Cost | $2,133.7 |
| Project Indirects & Construction Services | |
| Contractor Indirect Cost | $41.7 |
| Catering, Camp Operations & Maintenance | $94.6 |
| Contracted Services | $89.6 |
| Construction Equipment, Tools & Supplies | $14.6 |
| Freight & Duties | $59.3 |
| Field Startup & Vendor Services | $15.1 |
| Spares, Initial Fills (incl. Mining) | $65.5 |
| Project Indirect/ Project Management Labor | |
| EPCM Services | $139.2 |
| Owner's Cost | |
| Owner Project Team | $7.6 |
| Office Costs & Assets incl. vehicles | $0.6 |
| Owner Services Cost | $28.8 |
| Owner Preproduction G&A Costs | $104.7 |
| Opex During Ramp-up | $34.8 |
| Total Indirect Cost | $691.0 |
| Design Growth Allowances | $44.3 |
| Contingency | $293.9 |
| Total Capital Cost | $3,167.9 |
YPF Funding Power Supply
The construction cost of the Power Supply line to site and the electrical system upgrades total approximately $440 million which has not been included in the capital estimate as YPF Luz, a large Argentinean power utility company, will be constructing the line at their expense pursuant to a long-term, renewable power purchase agreement and connection repayment that will follow the terms agreed to in a Memorandum of Understanding.
To date, the company received preliminary finance proposals from Tier-1 OEMs and European export credit agencies for opportunities exceeding $1.1 billion for infrastructure and technology, covering 85 to 100% of major mechanical equipment and local installation costs - see the Strategic Partnerships section.
Operating Costs Estimates
Table 8 summarizes the LOM project operating costs per tonne of material processed and per pound of copper produced.
| Table 8: LOM Project Cash Costs | ||
| Description | LOM Cost/tonne ($) | LOM Cost/lb ($) |
| Mining | 6.22 | 0.87 |
| Processing | 3.83 | 0.54 |
| General & Administrative | 1.86 | 0.26 |
| Selling Expenses | 0.28 | 0.04 |
| LOM C1 Costs | 12.05 | 1.71 |
7. ESG & Sustainability
Environmental Highlights:
- Process water use : 159 L/s LOM average, 74% lower than a conventional mill producing copper concentrate with approx. 600 L/s(10). Peak Site Water use : 244.2 L/s, with 227 L/s allocated for mining activities and 17.2 L/s for human use. Electricity demand : 119 MW ( 48% lower than a concentrator ) GHG emissions : For the current project basis, the estimated annual average Green House Gas (GHG) emissions for the Los Azules project is 1,082 kg CO2-e/t Cu from Scope 1 and 2 sources. This places the project on the lowest decile of the copper industry carbon curve, well below the estimated industry average of 4,026 kg CO2-e/t Cu(5) using Skarn Associates mine-to-metal "E1" metric(13). At the start of operations, Los Azules will already be one of the lowest carbon copper cathodes produced in the world.
The project continues to develop electrification strategies for the mine and overall project including application of trolley assist for mine haulage, in-pit crushing and conveying and waste conveyance. The timing for these applications and others is under final analysis. Los Azules is also well positioned to take advantage of emerging opportunities (e.g. battery electric mine and services vehicles) and longer-term developing technologies. Goal : McEwen Copper is committed to becoming carbon neutral by 2038 at Los Azules, a target achievable using emerging technologies and offsets.
The project will source 100% renewable energy (wind, hydro, solar) and aims for net positive impacts on local ecosystems and communities.
8. Permitting & Regulatory Status
The Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) for Los Azules was granted on December 3, 2024.
On September 26, 2025, Los Azules was accepted into the Large Investment Incentive Regime RIGI. The investment regime provides the project with legal, fiscal, and customs stability for 30 years, including:
- Legal certainty, including tax, customs and foreign exchange stability for 30 years, with improved mechanisms in comparison with a prior regime applicable to mining activities, and access to international arbitration should a dispute arise.
Tax incentives in the investment phase -such as release from VAT payments which significantly reduces the financial burden during construction- and in the operation phase, such as the reduction of the corporate income tax rate to 25% from the general 35%, a 50% reduction in the dividend withholding tax, no export tax, an accelerated depreciation for new capital investments, and exemption from export duties. Streamlined customs procedures, including duty and tax exemptions to import of capital goods and the ability to leave export proceeds in foreign bank accounts, available to be applied to debt repayment or any other goal.
The Water Concession permit applications are currently under review with the provincial government. The use of heap leach technology, which is well accepted in San Juan Province, reduces permitting complexity by eliminating tailings and conserving water.
9. Nuton® Opportunity
Nuton is a technology venture of Rio Tinto that became a strategic partner of McEwen Copper in 2022. The Nuton® Technology is a suite of proprietary technologies that provide opportunities to leach both primary and secondary copper sulfides, providing a significant opportunity to optimize mine plans and overall mining and processing operations. In addition, Nuton® Technology provides significant other benefits, such as lower overall energy consumption, lower CO2 emissions, smaller land footprint, and lower water consumption per unit of copper produced than conventional sulfide mineralization recovery processes.
Based on strategic planning work by Whittle Consulting and considering the inferred resources, the use of Nuton offers the opportunity to extend the mine life beyond conventional leaching by 30 years or more.
Based on preliminary scoping testing, the Nuton® Technology offers the potential for copper recoveries of up to 85% on primary copper sulfide ore bodies, depending on the specific mineralogy make-up of the mineral resource. At Los Azules, the Nuton®Technology has the potential to economically process the large primary sulfide copper resource as an alternative to a concentrator, with low incremental capital following the oxide and supergene leach, no tailings requirement, and a smaller environmental footprint. Producing copper cathode with Nuton® on-site also has the advantage of simplifying outbound logistics in comparison to copper concentrates and offers a finished product to the domestic and international market.
The outcomes modelled using Nuton's proprietary computational fluid dynamics model are very encouraging and indicate that unoptimized copper recovery to cathode from primary material using Nuton® Technology should range from 73% to 79%. Furthermore, recovery from secondary material using Nuton® Technology is high, ranging from 80% to 86%. This could provide a significant opportunity to optimize the mine plan and reduce the need for selective mining, as simultaneous stacking of both secondary and primary mineralization will not impact the copper recovery of either material type. Based on the current resource estimate, using Nuton® Technology in the project could have a significant positive impact on the expected life of the mine and the projected cashflow, without significantly increasing the initial capital investment required.
Column leaching of Los Azules composite samples at Nuton® facilities was completed in Q1 2024 and used to support modelled metallurgical recoveries. Testing has been completed at Nuton facilities with a Phase 2a program, developing process design criteria and evaluating performance tested at a 10 m tall, large column scale. Fully mass balanced results are expected to be completed in Q4 2025. Preliminary assessment of the assay data suggests similar results to those provided in the PEA document. Besides refining and validating modelled data through additional column testing for Los Azules, Nuton is progressing an industrial-scale deployment at the Johnson Camp Mine (JCM) owned and operated by Gunnison Copper Corporation Inc. in Arizona, USA. This deployment's aim is to validate the Nuton® Technology package, from design and engineering to commissioning and operation, and to de-risk future Nuton deployments like the potential one at Los Azules.
McEwen Copper and Nuton are actively collaborating to deploy the Nuton® Technology at Los Azules. While a formal commercial agreement is not yet in place, both parties are committed to working in good faith toward establishing such an arrangement.
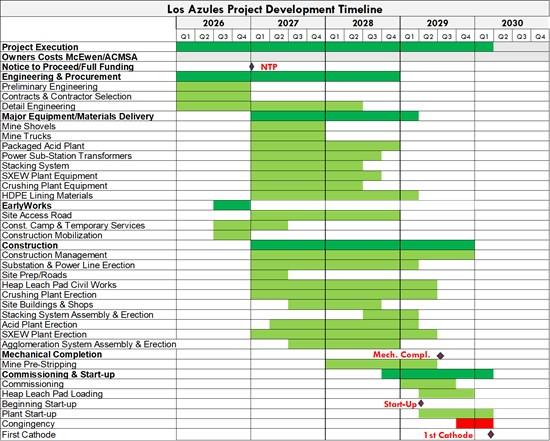
10. Development Timeline
The Gantt chart below presents a simplified project development timeline based on regional contractor inputs and long-lead equipment and materials delivery assumptions provided by vendors.
The schedule assumes that the feasibility study work is completed in October 2025, necessary permits to begin work are completed, and initial financing is in place to achieve the scheduled milestones.
Following this Level 3 schedule, the SX/EW plant could start in 2029, and the first cathode would be produced in 2030.
Figure 5: - Gantt Chart for Los Azules Project Development Timeline
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
11. Strategic Partnerships
McEwen Copper partnered with Nuton to evaluate the application of Nuton®Technology for the treatment of primary mineralization at the Los Azules project. Nuton also holds a 17.2% equity stake in McEwen Copper.
Stellantis, the world's fifth largest automaker, is also a strategic shareholder with an 18.3% interest. The partnership includes a copper cathode and concentrates purchase rights agreement and a joint commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2038.
As of the date of this release, McEwen Copper has received preliminary finance proposals with referential conditions from Tier 1 OEMs including, Komatsu, and Sandvik, as well as from European export credit agencies, covering 85 to 100% of the major mechanical equipment and 50% of the local construction cost for the project. The Argentine power company YPF Luz has signed an agreement with Los Azules to provide financing for the upgrades to the power grid and the power supply to the mine site and has agreed to provide 100% renewable power to the project. These proposals open the opportunity to finance more than $1.1 billion in investments for the crushing and handling system, SX/EW plant, acid plant, drilling fleet, and hauling and loading mining fleet, incorporating state-of-the-art technologies that support our regenerative guiding principles and commitment to sustainable innovation.
In September 2025, McEwen Copper announced that it had signed a collaboration agreement with the International Finance Corporation (IFC), a member of the World Bank Group, to support the alignment of the Los Azules copper project with IFC's ESG standards for potential future financing. This represents an important milestone in the company's broader financing strategy, helping to align the project with top-tier sustainability standards while paving the way for IFC as a potential lead lender and equity partner.
12. Study Contributors and Qualified Persons
The FS Technical Report is prepared in accordance with the requirements set forth by Canadian National Instrument 43-101 ("NI 43-101") for the disclosure of material information and is intended to meet the requirements of a Feasibility Study (FS) level of study and disclosure as defined in the regulations and supporting reference documents. The effective date of the report is September 3, 2025.
The report was prepared by Samuel Engineering Inc., with contributions from Knight Piésold Consulting, AGP Mining Consultants Inc, Nuton, a Rio Tinto Venture, E-Mining Technology S.A., Call & Nicholas, Inc., Itasca Consulting Group, Inc., CRM-SA, LLC, McLennan Design/Perkins&Will, Whittle Consulting Pty Ltd, Techint S.A.C.I., BW Hidrogeología y Medioambiente, and SRK Consulting UK Limited, under the supervision of David Tyler, McEwen Copper Project Director.
The feasibility study and associated disclosures have been reviewed and verified by the following qualified persons under NI 43-101 - Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects:
- Technical aspects of this news release related to Project Execution, Development information, and other information excluding mineral resource disclosure, have been reviewed and verified by James L. Sorensen - FAusIMM Reg. No. 221286 with Samuel Engineering. Technical aspects of this news release related to McEwen information, and other information excluding mineral resource disclosure, have been reviewed and verified by David Tyler - SME Registered Member. No. 3288830. He is the Project Director of the Los Azules Project and is not independent of the issuer. Technical aspects of this news release related to Metallurgical Summary and Process Information, have been reviewed and verified by Michael McGlynn - SME Registered Member No. 4149430 with Samuel Engineering. Disclosure related to the updated Los Azules mineral resource estimate has been reviewed and approved by Jeff Sullivan - FAusIMM Reg. No. 201778 with CRM-SA, LLC. Disclosure related to the initial Los Azules mining, and mineral reserve estimate has been reviewed and approved by Gordon Zurowski, P.Eng with AGP Mining Consultants. Technical aspects of this news release related to Financial Modeling, have been reviewed and verified by Steve Pozder - P.E. with Samuel Engineering.
13. End Notes
(8) Project capital intensity is defined as Initial Capex ($) / LOM Avg. Annual Copper Production (lbs or tonnes per year) or as LOM Capex ($) / LOM Copper Production (lbs or tonnes). C1 cash costs per pound produced is defined as the cash cost incurred at each processing stage, from mining through to recoverable copper delivered to the market, net of any by-product credits. All-in sustaining costs (AISC) per pound of copper produced adds production royalties, non-recoverable VAT and sustaining capital costs to C1. AISC margin is the ratio of AISC to gross revenue. Capital intensity, C1 cash costs per pound of copper produced, AISC per pound of copper produced, and AISC margin are all non-GAAP financial metrics. Numbers may not total due to rounding.
(9) Annual earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA). EBITDA is a non-GAAP financial measure.
(10) 2017 NI 43-101 Technical Report on Los Azules Project, Hatch Engineering (Throughput of 120,000 tpd of mineralized material).
(11) 2023 NI 43-101 Technical Report on Los Azules Project, Samuel Engineering.
(12) Kilograms of Carbon Dioxide Equivalent per tonne of Copper Equivalent produced. Carbon Dioxide Equivalent means having the same global warming potential as any other greenhouse gas.
(13) Skarn Associates Copper Mine GHG and Energy Intensity Curve Generator, June 2025 dataset for the year 2030. The E1 metric includes all GHG emissions from mine to refined metal. Skarn recommends E1 intensity as the most suitable metric for comparing operations, allowing SXEW and concentrate producers to be evaluated on the same curve, at the same product boundary - refined copper cathode."
For further details, visit the McEwen website.
Qualified Persons
The McEwen Copper feasibility study technical report has an effective date of September 3, 2025.
The feasibility study and associated news disclosures were reviewed and verified by the following qualified persons who are independent consultants of McEwen Copper:
- Technical aspects of the news release related to Project Execution, Development information, and other information excluding mineral resource disclosure - James L. Sorensen - FAusIMM Reg. No. 221286 with Samuel Engineering. Technical aspects of the news release related to Metallurgical Summary and Process Information - Michael McGlynn - SME Registered Member No. 4149430 with Samuel Engineering. Disclosure related to the updated Los Azules mineral resource estimate - Jeff Sullivan - FAusIMM Reg. No. 201778 with CRM-SA, LLC. Disclosure related to the initial Los Azules mining, and mineral reserve estimate - Gordon Zurowski, P.Eng with AGP Mining Consultants. Technical aspects of the news release related to Financial Modeling - Steve Pozder - P.E. with Samuel Engineering.
The McEwen press release appears to be reviewed and verified by a Qualified Person (as that term is defined by National Instrument 43-101 - Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects) and the procedures, methodology and key assumptions disclosed therein are those adopted and consistently applied in the mining industry, but no Qualified Person engaged by TNR has done sufficient work to analyze, interpret, classify or verify McEwen's information to determine the current mineral resource or other information referred to in its press releases. Accordingly, the reader is cautioned in placing any reliance on the disclosures therein.
Kirill Klip, the Company's Chief Executive Officer, stated, "We are pleased that McEwen Copper has reached this major milestone releasing feasibility study after it secured an environmental permit for the construction and operation of the Los Azules copper project. Feasibility study confirms that Los Azules copper is economically robust project with leading ESG performance. The collaboration between McEwen Copper and IFC, and admission to the Argentina Regime of Incentives for Investment (RIGI) could move the Los Azules copper project development closer to a construction decision.
"The new president of Argentina has introduced important government policies aimed at supporting business and unlocking the country's economic potential. Mining in Argentina is being recognized by the government as an integral part of its economic development plan, providing jobs and enriching local communities.
"Our Company has repaid our investment loan in full, and we believe that the recent market prices of our shares do not properly reflect the underlying value of TNR's assets. Our transformation from a project generation junior mining company into a cashflow-generating royalty company may bring the necessary catalyst for improved market valuation of our assets.
"Significant developments on the advancement of the Los Azules project towards the feasibility stage have led to increased Rio Tinto and Stellantis holdings in McEwen Copper, strategic partners of this large copper, gold and silver project. In 2023, Stellantis invested an aggregate ARS $72 billion. An additional US $100 million in total was invested by Rio Tinto's Venture Nuton® in McEwen Copper. TNR Gold's vision is aligned with the leaders of innovation among automakers like Stellantis, whose aim is to decarbonize mobility, and mining industry leaders such as Rob McEwen, whose vision is 'to build a mine for the future, based on regenerative principles that can achieve net zero carbon emissions by 2038'.
"Together with Nuton®, McEwen Copper is exploring new technologies that save energy, water, time and capital, advancing Los Azules towards the goal of leading environmental performance. The involvement of Rio Tinto, with its innovative technology, may also accelerate realizing the potential of the Los Azules project.
"The green energy rEVolution relies on the supply of critical metals like copper. Delivering 'green copper' to Argentina and the world will contribute to the clean energy transition and electrification of transportation and energy industries.
"The feasibility study confirms Los Azules project as a long-life, low-cost producer of high-purity copper cathodes with strong economic returns and sustainability. It highlights the potential to create a robust leach project while reducing the environmental footprint, and greater environmental and social stewardship sets the project apart from other potential mine developments.
"Los Azules was ranked in the top ten largest undeveloped copper deposits in the world by Mining Intelligence (2022). TNR Gold does not have to contribute any capital for the development of the Los Azules Project. The essence of our business model is to have industry leaders like McEwen as operators on the projects that will potentially generate royalty cashflows to contribute significant value for our shareholders."
ABOUT TNR GOLD CORP.
TNR Gold Corp. is working to become the green energy metals royalty and gold company.
Our business model provides a unique entry point in the creation of supply chains for critical materials like energy metals that are powering the energy rEVolution, and the gold industry that is providing a hedge for this stage of the economic cycle.
Our portfolio provides a unique combination of assets with exposure to multiple aspects of the mining cycle: the power of blue-sky discovery and important partnerships with industry leaders as operators on the projects that will potentially generate royalty cashflows to contribute significant value for our shareholders.
Over the past twenty-nine years, TNR, through its lead generator business model, has been successful in generating high-quality global exploration projects. With the Company's expertise, resources and industry network, the potential of the Mariana Lithium Project and Los Azules Copper Project in Argentina, among many others, have been recognized.
TNR holds a 1.5% NSR royalty on the Mariana Lithium Project in Argentina, of which 0.15% of such NSR royalty is held on behalf of a shareholder of the Company. Ganfeng Lithium's subsidiary, Litio Minera Argentina (" LMA "), has the right to repurchase 1.0% of the NSR royalty on the Mariana Project, of which 0.9% is the Company's NSR royalty interest. The Company would receive CAN$900,000, and its shareholder would receive CAN$100,000 on the repurchase by LMA, resulting in TNR holding a 0.45% NSR royalty and its shareholder holding a 0.05% NSR royalty.
The Mariana Lithium Project is 100% owned by Ganfeng Lithium. The Mariana Lithium Project has been approved by the Argentina provincial government of Salta for an environmental impact report. Ganfeng officially inaugurated Mariana Lithium's start of production at a 20,000 tons-per-annum lithium chloride plant on February 12, 2025.
TNR Gold also holds a 0.4% NSR royalty on the Los Azules Copper Project, of which 0.04% of the 0.4% NSR royalty is held on behalf of a shareholder of the Company. The Los Azules Copper Project is being developed by McEwen.
TNR also holds a 7% NPR on the Batidero I and II properties of the Josemaria Project that is being developed by the joint-venture between Lundin Mining and BHP.
TNR provides significant exposure to gold through its 90% holding in the Shotgun Gold porphyry project in Alaska. The project is located in Southwestern Alaska near the Donlin Gold project, which is being developed by Novagold Resources. The Company's strategy with the Shotgun Gold Project is to attract a joint venture partnership with a major gold mining company. The Company is actively introducing the project to interested parties.
At its core, TNR provides a wide scope of exposure to gold, copper, silver and lithium through its holdings in Alaska (the Shotgun Gold porphyry project) and royalty holdings in Argentina (the Mariana Lithium project, the Los Azules Copper Project and the Batidero I & II properties of the Josemaria Project), and is committed to the continued generation of in-demand projects, while diversifying its markets and building shareholder value.
On behalf of the Board of Directors,
Kirill Klip
Executive Chairman

Legal Disclaimer:
MENAFN provides the
information “as is” without warranty of any kind. We do not accept
any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images,
videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information
contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright
issues related to this article, kindly contact the provider above.
Most popular stories
Market Research

- Crypto Market Update: Pepeto Advances Presale With Staking Rewards And Live Exchange Demo
- Kucoin Appeals FINTRAC Decision, Reaffirms Commitment To Compliance
- Cregis And Sumsub Host Web3 Compliance And Trust Summit In Singapore
- Chartis Research And Metrika Release Comprehensive Framework For Managing Digital Asset Risk
- Nodepay Launches Crypto's Largest Prediction Intelligence Platform
- Schoenherr Opens London Liaison Office As Gateway To Central Eastern Europe



















Comments
No comment