
403
Sorry!!
Error! We're sorry, but the page you were looking for doesn't exist.
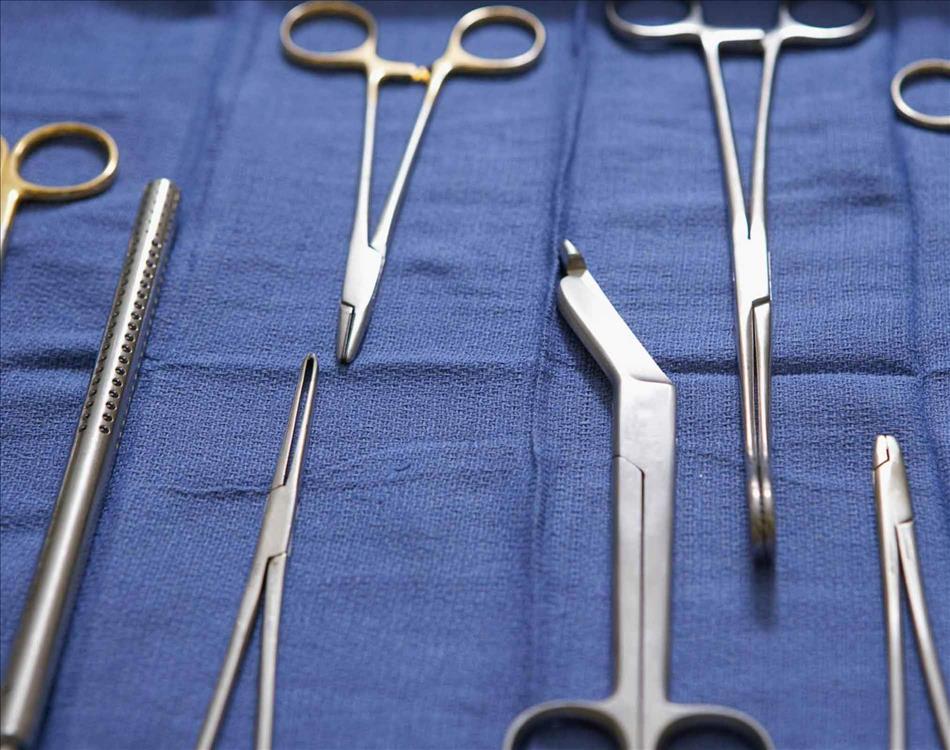
Surgical Clamps Find Application as Tools in Surgical Procedures to Control Bleeding
(MENAFN- Coherent Market Insights) Before we get into the discussion about surgical clamps, let's define what they actually are. A surgical clamp is a grasping apparatus or instrument for carrying out specific tasks or carrying out pre-determined outcomes during an operation or surgery, for example changing human organ tissues, or for viewing it under the microscope. Surgical clamps, over time, have evolved into many different types. There are clamps that hold the head of a needle, there are clamps that secure a ventilator in the lungs, and there are clamps that fix a dresser in place. They come in different shapes and sizes and perform different jobs.
For the purposes of this article we will focus on the most common surgical clamp styles used today. As already mentioned, there are many different types of these devices. However, the two most common surgical clamps to be found today are the reactor type and the blood flow clamp. Retractors are simply large clamps that can be wound up and which holds tissue out of the way for better blood flow. They come in both spring and continuous wire styles.
These devices are used most commonly for suturing and stitching, although many surgeons also use them for manually controlling incisions. The most popular style of retractor surgical clamp is the retractor-style forceps. These are designed to be used with light pressure (as in the case of a wound clamp) or by employing heavy tension. Medical grade retractor forceps have been proven to significantly reduce surgical scars. The blood flow clamps, on the other hand, use a long thin pole to draw blood away from a cut and deliver it into a bag attached to the forceps.
Forceps are used to pull the skin, tendons, bones or muscle away from areas where they are needed. Many people confuse them with retractors, but in actuality forceps have a very different function. Forceps are specifically designed to be used in cosmetic and plastic surgery applications. Forceps come in both continuous wire and spring styles. Spring forceps are used more commonly, although continuous wire and single action retractors are also available.
Both of these devices are used to manipulate tissues and apply traction to prevent damage to tissues. Forceps are normally used when skin grafts are required as well as surgical instruments to be grasped and moved. In addition, forceps are sometimes combined with scissors to form clippers and can even be used to cut and remove skin grafts. Surgeons typically combine all three of these tools to perform a variety of surgical procedures.
Another commonly used surgical clamp is the hemostat. Hemostats are similar to those used for blood flow during the surgical process. However, hemostats are also commonly used to keep the patient elevated while the procedure is taking place. This ensures that the patient will remain more stable and is less likely to pass out or be unable to catch their breath during the procedure. The difference in a hemostat and a retractor is that the former is designed to keep the blood flow moving at all times and prevent the patient from moving.
All three types of surgical clamps are used in conjunction with one another in order to properly manipulate and hold tissue. For example, forceps and clamps that are designed to be used together to ensure that proper grasping and maneuvering of the surgical instruments is possible without the risk of damaging the instruments. These tools also work together to ensure that excess blood flow is kept going and that excessive bleeding does not occur. If forceps and clamps were not designed to be used in conjunction with one another then this could lead to medical issues and possible injury to the patient if abnormal tissue growth occurred.
For the purposes of this article we will focus on the most common surgical clamp styles used today. As already mentioned, there are many different types of these devices. However, the two most common surgical clamps to be found today are the reactor type and the blood flow clamp. Retractors are simply large clamps that can be wound up and which holds tissue out of the way for better blood flow. They come in both spring and continuous wire styles.
These devices are used most commonly for suturing and stitching, although many surgeons also use them for manually controlling incisions. The most popular style of retractor surgical clamp is the retractor-style forceps. These are designed to be used with light pressure (as in the case of a wound clamp) or by employing heavy tension. Medical grade retractor forceps have been proven to significantly reduce surgical scars. The blood flow clamps, on the other hand, use a long thin pole to draw blood away from a cut and deliver it into a bag attached to the forceps.
Forceps are used to pull the skin, tendons, bones or muscle away from areas where they are needed. Many people confuse them with retractors, but in actuality forceps have a very different function. Forceps are specifically designed to be used in cosmetic and plastic surgery applications. Forceps come in both continuous wire and spring styles. Spring forceps are used more commonly, although continuous wire and single action retractors are also available.
Both of these devices are used to manipulate tissues and apply traction to prevent damage to tissues. Forceps are normally used when skin grafts are required as well as surgical instruments to be grasped and moved. In addition, forceps are sometimes combined with scissors to form clippers and can even be used to cut and remove skin grafts. Surgeons typically combine all three of these tools to perform a variety of surgical procedures.
Another commonly used surgical clamp is the hemostat. Hemostats are similar to those used for blood flow during the surgical process. However, hemostats are also commonly used to keep the patient elevated while the procedure is taking place. This ensures that the patient will remain more stable and is less likely to pass out or be unable to catch their breath during the procedure. The difference in a hemostat and a retractor is that the former is designed to keep the blood flow moving at all times and prevent the patient from moving.
All three types of surgical clamps are used in conjunction with one another in order to properly manipulate and hold tissue. For example, forceps and clamps that are designed to be used together to ensure that proper grasping and maneuvering of the surgical instruments is possible without the risk of damaging the instruments. These tools also work together to ensure that excess blood flow is kept going and that excessive bleeding does not occur. If forceps and clamps were not designed to be used in conjunction with one another then this could lead to medical issues and possible injury to the patient if abnormal tissue growth occurred.

Legal Disclaimer:
MENAFN provides the
information “as is” without warranty of any kind. We do not accept
any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images,
videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information
contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright
issues related to this article, kindly contact the provider above.

















Comments
No comment