
Qatar- All you need to know about symptoms, complications and vaccines of Flu
(MENAFN- Gulf Times) Qatar generally has a very hot and humid climate during the summers and is very cold during the winters. This year, the summer posed serious health concerns as the high humidity and soaring temperatures affected human lives. Now the school vacation has come to the end and many of the schools will reopen by the last week of this month. Many of the infectious diseases among students are very common in the time of climate change. So every parent needs to be aware these conditions. Influenza is by far the most common disease during the climate change in Qatar.
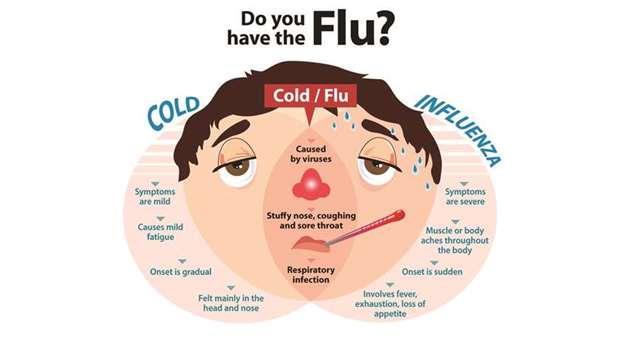
Influenza, commonly known as ‘the flu', is an infectious disease caused by the influenza virus. Symptoms can be mild to severe. The most common symptoms, include a high fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pains, headache, cough, and feeling tired. These symptoms typically begin two days after exposure to the virus and last for less than a week. The cough, however, may last for more than two weeks. In children there may be nausea and vomiting but these are not common in adults.
For most people, influenza resolves on its own, but sometimes influenza and its complications can be deadly. People at higher risk of developing flu complications, include children under 5 years of age especially those under 2, adults older than 65, residents of nursing homes and other long-term care facilities, pregnant women, people with a compromised immune system, people who have chronic illnesses, such as asthma, heart disease, kidney disease and diabetes, and people who have morbid obesity, with a body mass index (BMI) of 40 or higher
Usually, the virus spreads through air via coughing or sneezing. This is believed to occur mostly over relatively short distances. It can also be spread by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus, like door handles, and then touching the mouth or eyes. A person may be infectious to others both before and during the time they are sick. The infection may be confirmed by testing the throat, sputum, or nose for the virus.
Causes:
Influenza is a cold weather illness. This is because the influenza virus is transmitted through airborne respiratory droplets that have been introduced into the air through coughing and sneezing. When a person who has influenza coughs or sneezes, he/she propels the virus into the surrounding air which is then inhaled by others.
When a child is infected with viral fever, close proximity with other children results in faster transmission of the virus, resulting in several others being infected. The immunity in a child is low as compared to an adult hence the chance of being infected is extremely high. Closed environment is another reason for the spread of the infection.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of influenza can start within one to two days of infection. Usually the first symptoms are chills or sensation of feeling cold, but fever is also common early in its course, with body temperatures ranging from 38 to 39°C. Many people are so ill that they are confined to bed for several days, with aches and pains throughout their body, which are worse in their backs and legs. Symptoms of influenza may include:
1. Fever and extreme coldness
2. Cough
3. Nasal congestion
4. Runny nose
5. Sneezing
6. Body aches, especially joints and throat
7. Fatigue
8. Headache
9. Irritated, watering eyes
10. Reddened eyes, skin (especially face), mouth, throat and nose
11. Petechial rash
It can be difficult to distinguish between the common cold and influenza in the early stages of these infections, but flu can be identified by a high fever with a sudden onset and extreme fatigue. Influenza is a mixture of symptoms of common cold and pneumonia, body ache, headache, and fatigue.
Diarrhoea is not normally a symptom of influenza in adults, although it has been seen in some human cases of the H5N1 ‘bird flu'and can be a symptom in children.
Preventions:
1. In case of a child suffering from influenza, parents must ensure that the child is not send to day care or school.
2. Parents must ensure that their children avoid mingling with an infected child.
3. Hygiene is also extremely essential as it ensures a healthy living. Wash your hands often with soap and water or an alcohol-based hand rub
4. When the climate conditions have worsened, especially when it's dusty and windy, it is safer for the children to be indoors.
5. Try taking warm food and avoid cold items. Nutrition is very important and must focus on high protein and calorie diet.
6. Warm clothing is a necessity, preferably covering the whole body. Wearing mufflers, gloves and socks should be made compulsory for children below 10 years when going outdoors.
7. Avoid touching your eyes, nose, or mouth. Germs spread this way.
8. Try to avoid close contact with sick people.
9. Practice healthy habits. Get adequate sleep and exercise, manage your stress, drink plenty of fluids, and eat healthy and nutritious diet.
10. Cover your nose and mouth with a tissue paper when you cough or sneeze. Throw the paper in the trash after you use it.
11. Flu vaccines are available. Immunisation at the correct time is extremely important. It is better to be taken during the months between September November. It is very safe and has no side effects. It is highly recommended that children above the age of 6 months be vaccinated (especially those going to day cares). For children who have not been vaccinated earlier, 2 doses of vaccine separated by at least 4 weeks, and for others, one vaccination every year is recommended.
lDr Jacob Thomas is a Neonatologist and Paediatrician at Aster Hospital, Doha.

Legal Disclaimer:
MENAFN provides the
information “as is” without warranty of any kind. We do not accept
any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images,
videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information
contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright
issues related to this article, kindly contact the provider above.

















Comments
No comment