(
MENAFN- Newsfile Corp) Solis Completes 4th Hole - Planning Follow-up Drilling at Mostazal Copper Project, Chile
- Hole four successfully intersected widespread copper sulphide mineralisation from surface to bottom of hole at 446 metres.
- First phase drilling now complete, with all holes intersecting copper sulphides, supporting potential for a very large copper system at Mostazal.
- All holes logged and sampled - assay results pending.
- Detailed deeper-penetrating geophysical survey in progress.
Vancouver, British Columbia--(Newsfile Corp. - April 7, 2022) - Solis Minerals Ltd. (ASX: SLM) (TSXV: SLMN) (FSE: 08W) (' Solis Minerals ' or 'the Company ') is pleased to announce it has completed the fourth hole in the first phase drilling campaign at the Company's Mostazal Copper Project in Chile (' Mostazal ' or ' the Project '). All four holes have now successfully encountered broad zones of copper sulphide mineralisation, for the most part starting from surface, supporting potential for the existence of a large copper system at Mostazal.
Logging of the Company's fourth diamond hole (MODD004) is now complete and indicates that the hole has intersected mainly porphyritic amygdaloidal and andesitic volcanic rocks, lesser volcanic breccia and aphanitic andesite to the bottom of the hole. Core logging highlighted widespread sulphide mineralisation from traces to +1% sulphides observed from the surface to the bottom of the hole. The sulphide minerals observed include chalcopyrite, bornite, primary chalcocite and lesser pyrite[1].
CEO Jason Cubitt commented:
'Drilling of our initial campaign at Mostazal was completed on time, on budget, and with significant intersections of copper sulphide mineralisation in all four holes. This first phase of drilling was designed to test the presence and extent of copper sulphide mineralisation in both previously explored near surface manto structures as well as a deeper 'feeder' target.
'It's clear from mineralisation observed in drill core that a large copper bearing system is present at depth and appears to be related to mineralisation reported near surface. We are encouraged by the potential size of the mineralised system at Mostazal, especially at depths never before tested on the project. We're looking forward to receipt of assay results, and have commenced planning the second phase of drilling.'
Hole MODD004 was a deep vertical hole drilled to 446.1m located due east of the main zone (refer to Appendix 1 Table 1 for collar location details) of the mantos mineralisation, where mineralisation is observed on surface and exposed in the small-scale underground mines. The fourth hole was designed to test the continuity of the manto style mineralisation to the eastern part of the Mostazal manto deposit area where very little drilling has previously occurred (see Figure 1 below).
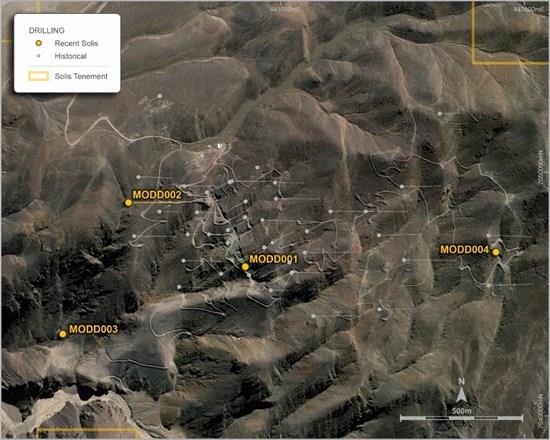
Figure 1: Mostazal Copper Project - Solis Minerals Ltd. diamond drill hole location plan
To view an enhanced version of Figure 1, please visit:
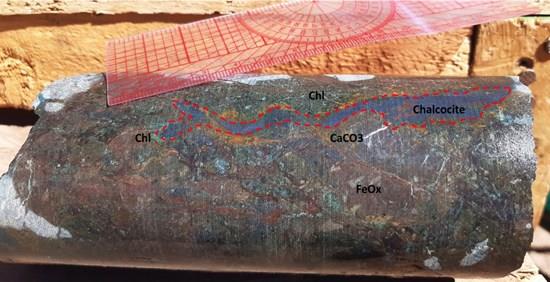
Figure 2: Hole 4 - Chalcocite veining encountered at depth of 35m
To view an enhanced version of Figure 2, please visit:
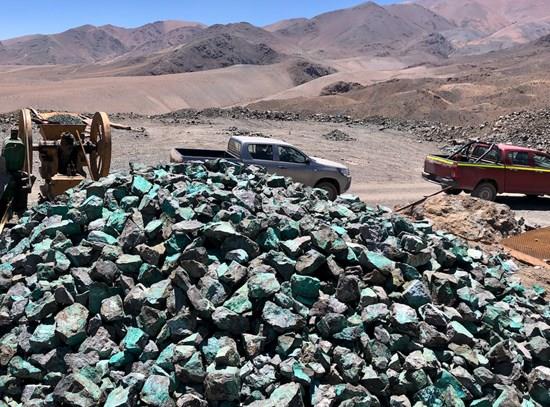

Figure 3: Excavations made by artisanal miners near MODD004 showing the presence of copper oxide mineralisation (green staining)
To view an enhanced version of Figure 3, please visit:
Next Steps
While the Company awaits assays from the first four holes, it is currently conducting a more detailed and deeper-penetrating geophysical program, together with detailed structural and geological mapping, which, when combined with the pending assay results, will refine the targeting strategy for the second round of drilling at Mostazal.
Southernrock Geophysics based in Santiago, Chile has been engaged to conduct a geophysical survey, consisting of 12.9 line kilometres of Pole-Dipole Induced Polarisation ('PDIP') and Magnetotellurics ('MT'), and an additional 10.5 line kilometres of MT over previously surveyed IP lines. The program of combined PDIP and MT is now underway; the PDIP will provide resistivity and chargeability sections to an effective depth of investigation well below 500m from surface, while the MT will allow much deeper resistivity sections. This survey is expected to be completed by mid-April.
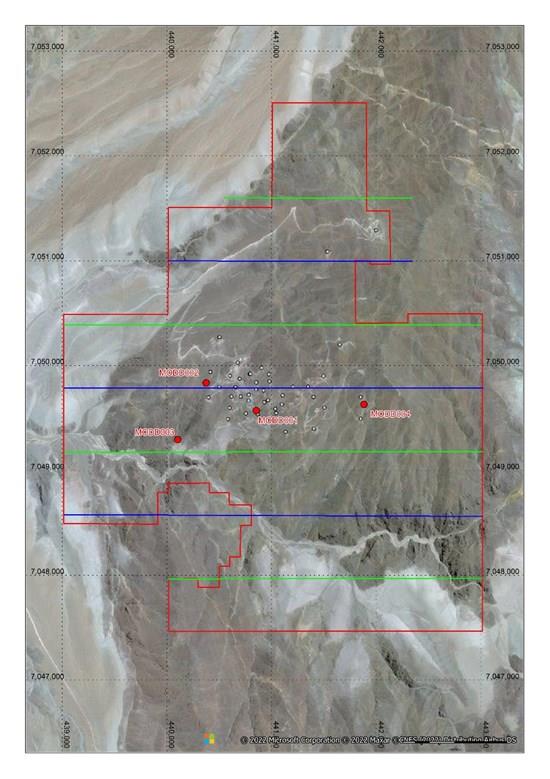
Figure 4: Mostazal Copper Project area, with proposed PDIP-MT survey lines (green), MT only lines (blue), property outline (in red)
To view an enhanced version of Figure 4, please visit:
This survey is designed to produce higher-fidelity modelling of the interpreted deep mineralised feeder system along the four-kilometre northeast trending IP chargeability zone identified in historic work. The survey will also provide a more comprehensive and deeper penetrating data set for the entire project area which will enhance the identification of both existing and new deep targets.
The Company has begun the drill permitting process for its second phase in anticipation of the resumption of drilling.
The high level of exploration activity across the industry, as well as ongoing impacts of COVID and the pressures that has placed on workforces and service providers has meant assays for the first holes are yet to be received by the Company. The Company is confident we will start to see these results in the next few weeks.
About Solis Minerals Ltd.
Solis Minerals is a Latin American-focused mining exploration company. The Company may earn up to a 100% interest in the Mostazal Copper Project in Chile's Atacama Desert, one of the world's premier copper production jurisdictions. The Company also holds a 100% interest in a package of highly prospective IOCG (iron oxide copper/gold) and porphyry copper projects in southwestern Peru within the country's prolific coastal copper belt - a source of nearly half of Peru's copper production.
Issued on the directive of the board of Solis.
For further information please contact:
Jason Cubitt
President and CEO
Solis Minerals Ltd.
+01 (604) 209 1658
Stephen Moloney
Investor Relations
Corporate Storytime
+61 (0)403 222 052
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Service Provider (as the term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy of accuracy of this news release.
Forward-Looking Statements
This news release contains certain forward-looking statements, which relate to future events or future performance and reflect management's current expectations and assumptions. Such forward-looking statements reflect management's current beliefs and are based on assumptions made by and information currently available to the Company. Readers are cautioned that these forward-looking statements are neither promises nor guarantees, and are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause future results to differ materially from those expected including, but not limited to, market conditions, availability of financing, actual results of the Company's exploration and other activities, environmental risks, future metal prices, operating risks, accidents, labour issues, delays in obtaining governmental approvals and permits, and other risks in the mining industry. All the forward-looking statements made in this news release are qualified by these cautionary statements and those in our continuous disclosure filings available on SEDAR at These forward-looking statements are made as of the date hereof and the Company does not assume any obligation to update or revise them to reflect new events or circumstances save as required by applicable law.
Qualified Person Statement
Fred Tejada, P. Geo. (30021), is a qualified person and a consultant to the Company and has reviewed and approved the technical content of this news release.
Competent Person Statement
The information in this ASX release in relation to Geological Information and Exploration Results is based on and fairly represent information compiled by Mr Anthony Greenaway, a Competent Person who is a Member of the Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy. Mr Greenaway is an employee of Solis Minerals Ltd. and has sufficient experience which is relevant to the style of mineralisation and types of deposit under consideration and to the exploration activities undertaken to qualify as a Competent Person as defined in the 2012 Edition of the 'Australian Code for Reporting of Mineral Resources and Ore Reserves'. Mr Greenaway consents to the inclusion in this report of the matters based on information in the form and context in which it appears. Mr Greenaway has provided his prior written consent as to the form and context in which the Geological Information and Exploration Results and supporting information are presented in this Announcement.
All information relating to exploration results that have been previously released to the market is appropriately referenced in this document.
APPENDIX 1
Table 1
Mostazal Copper Project Drill Collar Table
Hole
ID | Hole
Status | East
(m) | North
(m) | RL
(m) | Planned
(m) | EOH
(m) | DIP | AZI |
| MODD001 | Complete | 440,853 | 7,049,571 | 2748 | 500 | 362.0 | -90 | 0 |
| MODD002 | Complete | 440,374 | 7,049,835 | 2760 | 500 | 494.7 | -65 | 90 |
| MODD003 | Complete | 440,103 | 7,049,295 | 2521 | 500 | 528 | -90 | 0 |
| MODD004 | Complete | 441,881 | 7,049,630 | 2949 | 500 | 446.1 | -90 | 0 |
Table 2
Visual Estimates of Sulphide Mineralisation
| Hole ID | Depth From (m) | Depth To
(m) | Interval
(m) | Mineralisation Style | Sulphide Mineralisation | Estimated Sulphide
% |
| MODD004 | 1.70 | 3.90 | 2.2 | Fractures (ox); vnlts (sulph) and amygdales | Chalcopyrite>bornite>>chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 24.50 | 30.50 | 6 | Fractures (ox); vnlts (sulph) and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 30.50 | 31.60 | 1.1 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 31.60 | 33.00 | 1.4 | Fractures (ox); vnlts (sulph) and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 33.00 | 34.50 | 1.5 | Fractures (ox); vnlts (sulph) and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 34.50 | 35.90 | 1.4 | Fractures (ox); vnlts (sulph) and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite | 1-5% |
| MODD004 | 35.90 | 41.60 | 5.7 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 41.60 | 46.40 | 4.8 | Sulphide traces in calcite veins and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 46.40 | 51.00 | 4.6 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 51.00 | 56.15 | 5.15 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 56.15 | 58.60 | 2.45 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-Chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 59.27 | 60.00 | 0.73 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 60.00 | 63.90 | 3.9 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 63.90 | 67.80 | 3.9 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 67.80 | 70.30 | 2.5 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 72.15 | 84.80 | 12.65 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 86.40 | 94.80 | 8.4 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 94.80 | 100.80 | 6 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 100.80 | 101.15 | 0.35 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 101.15 | 108.00 | 6.85 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 113.00 | 118.00 | 5 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcocite-pyrite>chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 124.20 | 128.94 | 4.74 | Vnlts and amygdales | Bornite-chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 128.94 | 133.40 | 4.46 | Amygdales | Bornite > chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 128.94 | 134.33 | 5.39 | disseminated in cement of breccia | Bornite >> chalcopyrite | 1-5% |
| MODD004 | 134.33 | 143.15 | 8.82 | amygdales > veinlets | Bornite > > chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 146.40 | 149.10 | 2.7 | Amygdales | Bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 151.65 | 158.71 | 7.06 | Amygdales + veinlets | Bornite > chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 158.71 | 163.97 | 5.26 | On fractures >> disseminated | Chalcopyrite > bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 163.97 | 164.60 | 0.63 | Amygdales + veinlets | Bornite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 164.60 | 165.00 | 0.4 | Disseminated in breccia cement | Chalcopyrite > chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 165.00 | 168.24 | 3.24 | | | 0 |
| MODD004 | 168.24 | 169.50 | 1.26 | Amygdales | Chalcocite - bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 169.50 | 185.45 | 15.95 | On fracs | Chalcopyrite | Local tr |
| MODD004 | 185.45 | 188.40 | 2.95 | Disseminated > veinlets | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 188.40 | 190.23 | 1.83 | Amygdales | Bornite >> chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 190.23 | 192.40 | 2.17 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite >> chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 192.40 | 196.00 | 3.6 | Amygdales + veinlets | Bornite > chalcocite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 196.00 | 196.50 | 0.5 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 197.00 | 197.33 | 0.33 | Disseminated | Chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 197.80 | 198.40 | 0.6 | Amygdales >> veinlets | Bornite > chalcocite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 198.40 | 200.20 | 1.8 | Amygdales | bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 200.20 | 201.00 | 0.8 | Veinlets | Chalcopyrite > bornite >> chalcocite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 201.00 | 205.65 | 4.65 | Amygdales | Bornite > chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 205.65 | 207.10 | 1.45 | Veinlets > disseminated | Bornite > chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 207.10 | 212.00 | 4.9 | Veinlets + disseminated | Bornite > chalcopyrite >> chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 212.00 | 213.00 | 1 | Amygdales | Bornite > chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 213.00 | 214.49 | 1.49 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite >> bornite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 214.49 | 216.00 | 1.51 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite >> chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 216.00 | 217.00 | 1 | Amygdales | Chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 217.00 | 219.10 | 2.1 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite > chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 219.10 | 221.00 | 1.9 | In small hydrothermal breccia and amygdales | Chalcopyrite >> bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 221.00 | 224.83 | 3.83 | Disseminated + fracs (with chlorite) | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 224.83 | 228.10 | 3.27 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite + bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 228.10 | 230.00 | 1.9 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite + bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 230.00 | 231.30 | 1.3 | Amygdales | Bornite, chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 232.00 | 233.75 | 1.75 | amygdales > veinlets | Bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 240.10 | 244.60 | 4.5 | Amygdales + diss. | Bornite > chalcopyrite > chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 244.60 | 247.05 | 2.45 | Amygdales | Bornite >> chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 247.05 | 248.88 | 1.83 | Amygdales | Bornite, chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 248.88 | 249.15 | 0.27 | Amygdales | Bornite > chalcocite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 249.15 | 250.90 | 1.75 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 250.90 | 252.20 | 1.3 | Disseminated and in narrow stringers | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 252.20 | 253.34 | 1.14 | Disseminated an in veinlets | Chalcopyrite, pyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 253.34 | 253.70 | 0.36 | Veinlet | chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 262.77 | 266.06 | 3.29 | Disseminated (very local) | Bornite - chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 266.06 | 269.25 | 3.19 | Disseminated | Chalcopyrite; sphalerite (?) | Tr |
| MODD004 | 285.00 | 287.20 | 2.2 | Amygdales > veinlets | Bornite > chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 302.43 | 311.00 | 8.57 | Disseminated in amygdales and breccias | Bornite >> chalcopyrite > chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 312.10 | 318.10 | 6 | Amygdales | Bornite > chalcocite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 319.75 | 330.34 | 10.59 | Disseminated (very local) | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 330.34 | 334.57 | 4.23 | Disseminated >> veinlets | Chalcopyrite >> bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 334.57 | 341.20 | 6.63 | Disseminated | Chalcopyrite >> bornite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 341.20 | 347.65 | 6.45 | Amygdales >> veinlets | Chalcopyrite >> bornite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 347.65 | 348.10 | 0.45 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 348.10 | 355.24 | 7.14 | Disseminated (very local) | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 355.24 | 358.85 | 3.61 | Disseminated (very local) | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 358.85 | 361.70 | 2.85 | Amygdales (close to the lower contact only) | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 341.20 | 374.53 | 33.33 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 379.00 | 380.58 | 1.58 | veinlets (with chlorite) + disseminated | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 381.29 | 391.21 | 9.92 | Amygdales > veinlets | Chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 391.21 | 392.10 | 0.89 | Amygdales > veinlets | Chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 392.10 | 398.00 | 5.9 | Amygdales | Bornite, chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 399.54 | 401.42 | 1.88 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr5 |
| MODD004 | 401.42 | 405.14 | 3.72 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 405.14 | 408.89 | 3.75 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 408.89 | 415.04 | 6.15 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 415.04 | 416.82 | 1.78 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 416.82 | 424.88 | 8.06 | Amygdales | Chalcopyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 424.88 | 430.55 | 5.67 | Amygdales | Pyrite > chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 430.55 | 436.80 | 6.25 | Amygdales | Pyrite >> chalcopyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 436.80 | 440.20 | 3.4 | Diss. and in amygdales | Pyrite | Tr-1% |
| MODD004 | 440.20 | 442.40 | 2.2 | Amygdales and fractures | Pyrite | Tr |
| MODD004 | 443.00 | 446.10 | 3.1 | Amygdales | Pyrite | Tr-1% |
Cautionary note:
The Company stresses that the reported visually estimated percentages in Table 2 above, relate specifically to the abundance of sulphides logged in the drill core and is not an estimated grade for the interval.
In relation to the disclosure of visual results, the Company cautions that visual estimates of mineral abundance should never be considered a proxy or substitute for a laboratory analysis. Assay results are required to determine the widths and grade of the visual mineralisation in preliminary geological logging. The Company will update the market when laboratory results become available.
Figure 5: Mostazal Copper Project location
To view an enhanced version of Figure 5, please visit:
APPENDIX 2
JORC Code, 2012 Edition - Table 1
Section 1 Sampling Techniques and Data
(Criteria in this section apply to all succeeding sections)
| Criteria | JORC Code explanation | Commentary |
| Sampling techniques | - Nature and quality of sampling (e.g. cut channels, random chips, or specific specialised industry standard measurement tools appropriate to the minerals under investigation, such as down hole gamma sondes, or handheld XRF instruments, etc). These examples should not be taken as limiting the broad meaning of sampling.
- Include reference to measures taken to ensure sample representivity and the appropriate calibration of any measurement tools or systems used.
- Aspects of the determination of mineralisation that are Material to the Public Report.
- In cases where 'industry standard' work has been done this would be relatively simple (e.g. 'reverse circulation drilling was used to obtain 1 m samples from which 3 kg was pulverised to produce a 30 g charge for fire assay'). In other cases more explanation may be required, such as where there is coarse gold that has inherent sampling problems. Unusual commodities or mineralisation types (e.g. submarine nodules) may warrant disclosure of detailed information.
| - Sampling across the project has included rock chip sampling of open pit exposure, trenches, rock outcrops, soil sampling and diamond drilling.
- Soil, trenching and outcrop sampling was undertaken by Sociedad Legal Minera Mostazal between 2005 and 2008, Galileo Minerals Ltd in 2008, and IMT Exploraciones between 2011 and 2013.
- Diamond drilling was undertaken by IMT Exploraciones between 2012 and 2013.
- Soil sampling and rock chip sampling was used to identify zones of potential mineralisation.
- These is no detailed record of how outcrop sampling was completed or the size of the samples.
- Trenches were sampled on 1m intervals; however the size of the sample is not recorded.
- Diamond drill holes were samples on either 1 m, 3 m or 4 m, intervals as half core samples.
- Solis Minerals is completing a diamond drilling program at Mostazal, comprising up to 4,000m of diamond drill core.
|
| Drilling techniques | - Drill type (e.g. core, reverse circulation, open-hole hammer, rotary air blast, auger, Bangka, sonic, etc) and details (e.g. core diameter, triple or standard tube, depth of diamond tails, face-sampling bit or other type, whether core is oriented and if so, by what method, etc).
| - All historical drilling completed to date at the Mostazal Copper Project has been diamond drilling.
- 60 diamond drill holes were completed by previous explorers for a total of 11,381m.
- Historical diamond drilling was undertaken using a Boart Longyear LF-900 drilling rig. Drill holes were completed as HQ size (63.5mm core diameter). There is no record of the drill tube type used, i.e. triple tube or standard tube.
- Solis Minerals is completing HQ2 (63.5mm core diameter) diamond drilling utilising wirelines drilling techniques.
|
| Drill sample recovery | - Method of recording and assessing core and chip sample recoveries and results assessed.
- Measures taken to maximise sample recovery and ensure representative nature of the samples.
- Whether a relationship exists between sample recovery and grade and whether sample bias may have occurred due to preferential loss/gain of fine/coarse material.
| - Diamond core recovery was recorded for each sample interval by measuring the recovered core against the drill depth.
- Diamond core recovery varied between 0.25% and 100%, but typically averaged 95%.
- There is no apparent relationship between core recovery and grades from historical data.
- There is no apparent sample bias due to preferential loss/ gain of fine/ coarse material.
|
| Logging | - Whether core and chip samples have been geologically and geotechnically logged to a level of detail to support appropriate Mineral Resource estimation, mining studies and metallurgical studies.
- Whether logging is qualitative or quantitative in nature. Core (or costean, channel, etc) photography.
- The total length and percentage of the relevant intersections logged.
| - Rock chip and soil sampling was usually completed as part of a geological mapping campaign.
- Historical diamond drill holes were geologically logged at varying intervals based on lithology. Logging included, lithology, colour, mineralogy, texture, alteration, structure, mineralisation and RQD. All diamond drill core has been logged.
- Solis Minerals has logged all current drill holes in detail including lithology, colour, mineralogy, texture, alteration, structure, mineralisation and RQD.
|
| Sub-sampling techniques and sample preparation | - If core, whether cut or sawn and whether quarter, half or all core taken.
- If non-core, whether riffled, tube sampled, rotary split, etc and whether sampled wet or dry.
- For all sample types, the nature, quality and appropriateness of the sample preparation technique.
- Quality control procedures adopted for all sub-sampling stages to maximise representivity of samples.
- Measures taken to ensure that the sampling is representative of the in-situ material collected, including for instance results for field duplicate/second-half sampling.
- Whether sample sizes are appropriate to the grain size of the material being sampled.
| - Diamond core was cut using a core saw and sampled as either half core or quarter core.
- Soil and rock chip samples collected by Galileo Minerals Ltd were sent to Vigalab laboratory in Copiapo, whereas samples collected by IMP Exploraciones were sent to Andes Analytical Assay Ltda in Santiago for sample preparation and analysis. There are no records for rock chip samples and soil samples collected by Sociedad Legal Minera Mostazal.
- There is no detailed description of the sample preparation methods for the historical soil and rock chip samples.
- Diamond drill core was sent to Andes Analytical Assay Ltda in Santiago for sample preparation and analysis.
- There is no detailed description of sample preparation methods used for historical diamond drill core.
- Quality control samples were inserted into each of the soil, rock chip and diamond drilling sample batches and included field duplicates, blanks and certified reference material samples. There is no record of any internal laboratory quality control sampling.
- Solis Minerals drill core is being cut using a core saw and sampled as half core.
- Solis Minerals samples are being sent to ALS in La Serena Chile for sample preparation including crushing (70% <2mm), riffle splitting 1kg sub sample and fine pulverisation (85%<75um).
- Sample sizes are appropriate for the material being sampled.
|
| Quality of assay data and laboratory tests | - The nature, quality and appropriateness of the assaying and laboratory procedures used and whether the technique is considered partial or total.
- For geophysical tools, spectrometers, handheld XRF instruments, etc, the parameters used in determining the analysis including instrument make and model, reading times, calibrations factors applied and their derivation, etc.
- Nature of quality control procedures adopted (e.g. standards, blanks, duplicates, external laboratory checks) and whether acceptable levels of accuracy (i.e. lack of bias) and precision have been established.
| - There are no assay records for rock chip and soil samples for samples collected by Sociedad Legal Minera Mostazal.
- Rock chip and soil samples collected by Galileo Minerals Ltd were assayed for copper, soluble copper, solvent copper extraction from pregnant solution, gold silver, lead, zinc, molybdenum arsenic and iron. The analytical method is not recorded.
- Rock and soil samples collected by IMT Exploraciones were assayed for 39-elements using Inductively coupled mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).
- Diamond core samples were assayed for a 39-element suit using Inductively coupled mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).
- Quality control samples were inserted into each of the soil, rock and diamond drilling sample batches and included field duplicates, blanks and certified reference materials. There is no record of any internal laboratory quality control sampling.
- ICP-MS is considered to be a total assay method.
- 6,830 diamond core samples ranging in length from 0.04m to 20m were submitted for SG analysis using Archimedes method.
- Solis Minerals drill core samples are being assayed for a 33-element suite via 4 acid digestion with ICP-AES finish, as well as gold by 50gm fire assay/AAS.
- Solis Minerals routinely inserts reference standards and blanks and duplicates into the sampling system at a 1:25 frequency.
|
| Verification of sampling and assaying | - The verification of significant intersections by either independent or alternative company personnel.
- The use of twinned holes.
- Documentation of primary data, data entry procedures, data verification, data storage (physical and electronic) protocols.
- Discuss any adjustment to assay data.
| - Reported significant intersections have been calculated as length weighted averages by Soils Minerals.
- There have been no twin drill holes completed.
- There have been no adjustments made to the historical assay data.
|
| Location of data points | - Accuracy and quality of surveys used to locate drill holes (collar and down-hole surveys), trenches, mine workings and other locations used in Mineral Resource estimation.
- Specification of the grid system used.
- Quality and adequacy of topographic control.
| - Drill holes have been located using a handheld GPS (model unknown).
- Down hole surveys were conducted for each diamond drill hole on 50m intervals. There is no description of the survey tool used.
- All data has been collected in UTM zone 19S coordinates.
- The topography was surveyed on 1-5m contours intervals in 2012 over the entire project area by contract surveyors (method unknown).
- Artisanal open cut and underground mining occurred throughout the project area between 1950s and 2006. Sociedad Legal Minera Ltda then conducted a small scale open cut surface and room and pillar underground mining between 2006 and 2008. The surface mining has been surveyed during the topographic survey in 2012, however the underground workings have not been surveyed.
- Solis Minerals has located initial drill site via a hand held GPS, and will have final hole locations survey by an independent contractor.
- Solis Minerals reports all coordinates in PSAD56 - 19S.
|
| Data spacing and distribution | - Data spacing for reporting of Exploration Results.
- Whether the data spacing and distribution is sufficient to establish the degree of geological and grade continuity appropriate for the Mineral Resource and Ore Reserve estimation procedure(s) and classifications applied.
- Whether sample compositing has been applied.
| - Geological sampling (rock and soil) has been completed on a nominal 200m x 200m grid over the entire project area.
- Diamond drilling was previously completed over the central parts of the project area on a nominal 150m x 100m grid.
- The sampling data is sufficient to establish the general extents and orientation of the near surface manto copper-silver style mineralisation, however the mineralisation remains open along strike and at depth.
- Sample compositing has not been applied.
- Solis Minerals is undertaking selected drilling at this stage, with no set drill spacing.
|
| Orientation of data in relation to geological structure | - Whether the orientation of sampling achieves unbiased sampling of possible structures and the extent to which this is known, considering the deposit type.
- If the relationship between the drilling orientation and the orientation of key mineralised structures is considered to have introduced a sampling bias, this should be assessed and reported if material.
| - The historical diamond drilling was completed in three phases. The initial phase of drill holes were angled to the southwest and were fanned off drilling platforms spaced approximately 100m apart on a northwest-southeast line. The subsequent drilling programs were drilled steeply towards the east or northeast to intersect the manto structures at a perpendicular angle.
- Solis Minerals is drilling both vertical and angel holes designed to test specific targets. Drilling is designed to intersect the planned targets at a perpendicular angle.
|
| Sample security | - The measures taken to ensure sample security.
| - There is no detailed record of sample chain of custody between the project site and the assay laboratories for historical programs.
- Remnant drill core is securely stored at Sociedad Legal Minera Mostazal's property in Copiapo.
- Solis Minerals staff and contractors manage the movement on site, including the transport of cut samples from site to the laboratory in La Serena.
|
| Audits or reviews | - The results of any audits or reviews of sampling techniques and data.
| - There have been no detailed audits or reviews of the historical sampling techniques.
- Solis Minerals has conducted an internal technical review of the historical Mostazal Copper Project data.
|
Section 2 Reporting of Exploration Results
(Criteria listed in the preceding section also apply to this section)
| Criteria | JORC Code explanation | Commentary |
| Mineral tenement and land tenure status | - Type, reference name/number, location and ownership including agreements or material issues with third parties such as joint ventures, partnerships, overriding royalties, native title interests, historical sites, wilderness or national park and environmental settings.
- The security of the tenure held at the time of reporting along with any known impediments to obtaining a licence to operate in the area.
| - The Mostazal Copper Project is located in the commune of Diego de Almagro, in the Chañaral Province of the Third Atacama Region, Chile approximately 80km northeast of the city of Copiapo.
- The Mostazal Copper Project consists of eight Exploitation Mining Concessions covering an area of 1,317 ha that were constituted in accordance with the Chilean mining Code 1993.
- The eight concessions are currently 100% owned by a series of legal Mining Companies (Sociedad Legal Minera), each of which are owned by two shareholders, who are also the owners of Sociedad Legal Minera Mostazal.
|
| Exploration done by other parties | - Acknowledgment and appraisal of exploration by other parties.
| - Sociedad Legal Minera Mostazal completed reconnaissance sampling and mining activities at the project between 2005 and 2008.
- Galilea Minerals conducted trench and outcrop sampling in 2008 and produced an exploration target for the M-01 mineralised lens based upon previous geological mapping and surface sampling.
- IMT Exploraciones completed soil, trench and outcrop sampling, diamond drilling, and ground magnetic and induced polarization geophysical surveys between 2011 and 2013.
- APGC Corp Chile Spa produced a foreign estimate for the Mostazal Copper Project in 2015 using the diamond drilling data, surface sampling and mapping.
- Santiago Metals Limitada completed geological mapping over the project area in 2016.
|
| Geology | - Deposit type, geological setting and style of mineralisation.
| - The Mostazal Copper Project area consists of fine grained to porphyritic andesite lava flows and breccias of the Jurassic - lower Cretaceous age Sierra Fraga Formation, that are locally interbedded with volcaniclastic sediments. The andesites are intruded by a series of dacite porphyry dykes of Paleocene to Eocene age that typically trend northeast - southwest. The western and southeastern portions of the project area covered by late-stage Tertiary Atacama gravels with thicknesses ranging from a few metres to a few tens of metres. More recent Quaternary age sediments including sand, gravel, colluvium, and silt cover occurs throughout the project area.
- Mineralisation identified at the Mostazal Copper Project consists of several stacked stratified and discontinuous copper-silver (Cu-Ag) mineralised lenses or 'mantos' within the andesitic volcanic rocks that strike to the north-northwest and dip to the west, subparallel to the host andesite flow banding.
|
| Drill hole Information | - A summary of all information material to the understanding of the exploration results including a tabulation of the following information for all Material drill holes:
- easting and northing of the drill hole collar
- elevation or RL (Reduced Level - elevation above sea level in metres) of the drill hole collar
- dip and azimuth of the hole
- hole length
- If the exclusion of this information is justified on the basis that the information is not Material and this exclusion does not detract from the understanding of the report, the Competent Person should clearly explain why this is the case.
| - A summary of the current Mostazal drilling data/ hole locations is included in Table 1 of this document.
|
| Data aggregation methods | - In reporting Exploration Results, weighting averaging techniques, maximum and/or minimum grade truncations (e.g. cutting of high grades) and cut-off grades are usually Material and should be stated.
- Where aggregate intercepts incorporate short lengths of high-grade results and longer lengths of low-grade results, the procedure used for such aggregation should be stated and some typical examples of such aggregations should be shown in detail.
- The assumptions used for any reporting of metal equivalent values should be clearly stated.
| - Intersection have been calculated as length weighted averages.
- Selected intersections are reported above a nominal intersection grade cutoff of >0.5% Cu, with a maximum of 3m of internal dilution.
- No metal equivalent values have been used.
|
| Relationship between mineralisation widths and intercept lengths | - These relationships are particularly important in the reporting of Exploration Results.
- If the geometry of the mineralisation with respect to the drill hole angle is known, its nature should be reported.
- If it is not known and only the down hole lengths are reported, there should be a clear statement to this effect (e.g. 'down hole length, true width not known').
| - Calculated intersections are reported as down-hole widths. There is insufficient data at this to enable to calculation of true width intersections.
|
| Diagrams | - Appropriate maps and sections (with scales) and tabulations of intercepts should be included for any significant discovery being reported These should include, but not be limited to a plan view of drill hole collar locations and appropriate sectional views.
| - The Company has included various maps and figures showing the sample results and geological context.
|
| Balanced reporting | - Where comprehensive reporting of all Exploration Results is not practicable, representative reporting of both low and high grades and/or widths should be practiced avoiding misleading reporting of Exploration Results.
| - All analytical results for copper and silver, have been reported.
- Assay results for Solis Minerals' drilling are pending.
|
| Other substantive exploration data | - Other exploration data, if meaningful and material, should be reported including (but not limited to): geological observations; geophysical survey results; geochemical survey results; bulk samples - size and method of treatment; metallurgical test results; bulk density, groundwater, geotechnical and rock characteristics; potential deleterious or contaminating substances.
| - IMT Exploraciones completed ground magnetic and Induced polarization surveys over the project area.
|
| Further work | - The nature and scale of planned further work (e.g. tests for lateral extensions or depth extensions or large-scale step-out drilling).
- Diagrams clearly highlighting the areas of possible extensions, including the main geological interpretations and future drilling areas, provided this information is not commercially sensitive.
| - Solis Minerals will undertake extensive validation and field confirmation of the various targets identified from the historical data at the Mostazal Copper Project.
- A comprehensive work program for the Mostazal Copper Project has been proposed and will include additional diamond drilling, relogging and sampling of the existing diamond drill core, geological mapping and geophysics.
- Solis Minerals is currently undertaking a geophysical survey at Mostazal.
|
[1] Refer to Appendix 1 Table 2
To view the source version of this press release, please visit
MENAFN07042022004218003983ID1103976233




























Comments
No comment